In-House Servers vs Cloud Computing: What to Prefer?
Contents
Every business, whether a well-established corporation or a budding startup, reaches a pivotal moment where technology becomes a driving force for growth. Your enterprise is expanding, and you’re grappling with how to scale your IT infrastructure efficiently. Or you’re starting a new venture, and you’re keen to lay a solid technology foundation. In either scenario, choosing between in-house servers and cloud computing can set the stage for your future success. This article compares these technical solutions, providing insights to make the right choice.
What are In-House Servers and Cloud Computing
An in-house server, or an on-premise server, refers to a physical server infrastructure that a business owns, operates, and maintains within its own premises or data center. This dedicated computing system is used for storing, processing, and managing data and applications for internal use. In-house servers typically involve specific hardware, operating systems, and software applications configured to meet the organization’s computing needs.
Cloud hosting, in contrast, is a technology model that leverages remote servers, typically operated by third-party providers, to store, process, and manage data and applications. It runs on a cloud computing infrastructure that utilizes virtualization technology to create multiple virtual servers on shared physical hardware, offering scalable and flexible resources accessible over the internet.
In-house vs cloud servers: what is the difference
When comparing in-house servers to cloud computing, several key distinctions emerge:
- IT infrastructure
In-house servers are physically located on-site, requiring dedicated space within the organization’s premises. In contrast, cloud computing relies on remote servers managed by a service vendor, eliminating the need for physical infrastructure. - Data accessibility
On-premise servers offer local data access without the need for an internet connection. However, access is limited to on-site locations, restricting remote or mobile access. Cloud computing provides remote data accessibility, allowing users to access data from anywhere with an internet connection, enhancing flexibility and centralizing data. - Time savings
Cloud computing simplifies software management, as applications are browser-based and easily accessible from any device. In-house servers often require software installations on individual devices, necessitating IT support. - Security & data backup
Cloud providers typically offer advanced security measures, including intrusion detection, firewalls, and physical security. They often adhere to industry compliance standards to safeguard data. Additionally, cloud services often have robust data backup solutions, ensuring data recovery even in the face of disasters. Local servers require inherent security measures and cybersecurity, placing the responsibility on the owner. In-house operations may struggle with disaster recovery without remote co-location, potentially resulting in data loss and downtime. - Scalability
On-premise server scalability involves significant planning and investment, as physical space and hardware compatibility must be considered. Cloud platforms offer flexible scalability by default, allowing resources to be easily increased or decreased based on demand, with rapid provisioning. - Cost
In-house servers involve various costs, including hardware, staffing, energy, real estate, and ongoing maintenance. Cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to pay for the resources they use without the upfront capital expenditure. Serverless solutions have a lower total cost of ownership, especially for small to medium-sized businesses.
Pros and cons of in-house server
Advantages:
- In-house servers give businesses complete control over the physical server and their data. Knowing the location of your data can offer a sense of security.
- While the initial server setup is an expense, ongoing costs are primarily related to maintenance once you own the server, resulting in predictable spending.
- Storing data locally offers the security of being a distinct entity in the vast internet landscape, which can be appealing to those concerned about data safety.
Disadvantages:
- On-premise servers require sizing for peak loads, even if these peaks are infrequent. That necessitates a substantial upfront investment in hardware and licensing to handle occasional spikes in demand.
- Running a server 24/7/365 entails ongoing operating costs, including electricity and cooling, to maintain suitable server room temperatures, regardless of whether employees are in the building.
- Rapid business growth may lead to the need for more server capacity. However, if you outgrow your existing server, you may face the costly prospect of acquiring a new, larger server, resulting in significant expenses.
Pros and cons of cloud infrastructure
Advantages:
- Cloud infrastructure eliminates the need for a significant upfront investment in hardware and licensing, making it a cost-effective choice for startups and new businesses.
- Cloud-based servers enable employees to access data remotely from anywhere with internet connectivity, ensuring flexibility and accessibility.
- Cloud services allow for easy scalability, enabling businesses to adjust storage, memory, and resources to meet changing needs. You only pay for the resources you use, offering cost-efficiency.
- Cloud providers typically have extensive experience in safeguarding servers, often offering better security measures compared to internal IT departments.
Disadvantages:
- Cloud infrastructure operation depends on a reliable internet connection. When the internet is down, access to cloud-based servers becomes unavailable, potentially requiring a backup internet connection for uptime.
- While cloud platforms offer robust solutions, the long-term hosting costs might surpass those of in-house servers for high-uptime requirements. A 99.99% uptime solution with in-house servers would be expensive, but cloud servers can increase hosting expenses over time.
- Relying on hosting companies for security can be a concern, especially when you may never meet them and they are located remotely. Building trust in a cloud provider’s security measures is essential for peace of mind.
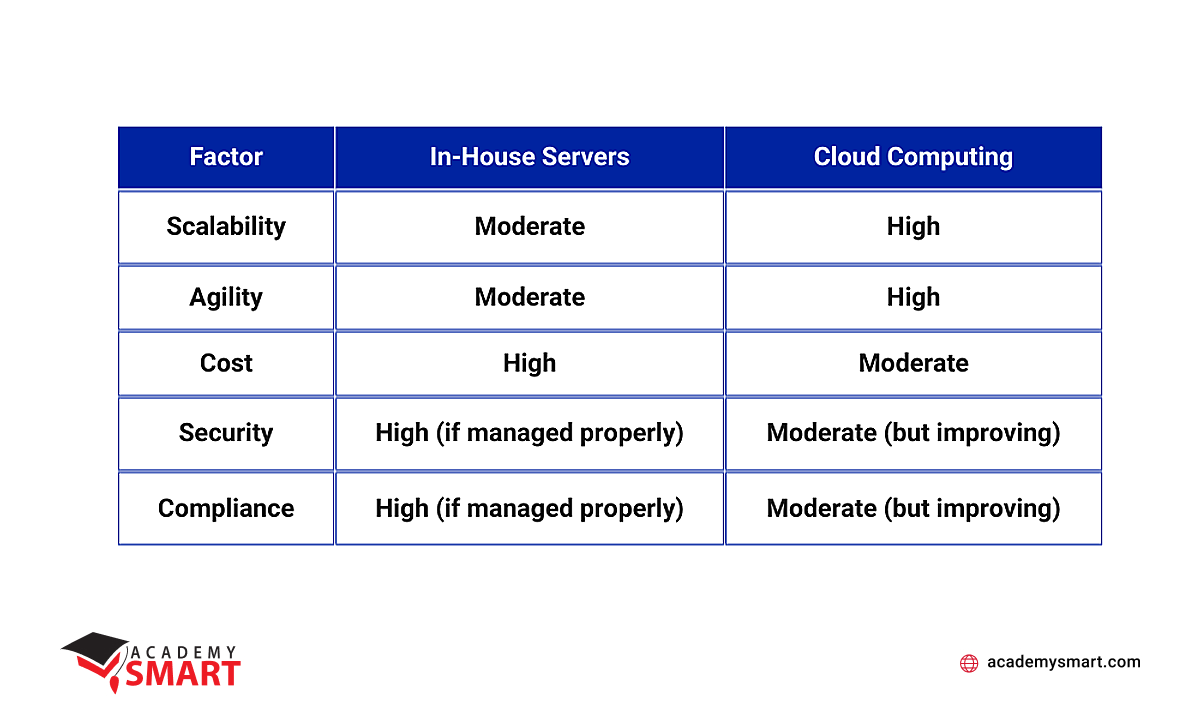
Comparison of in-house servers vs cloud computing
When to Use Cloud vs In House Server
Cloud infrastructure is an excellent choice when you need easy access to data from anywhere with an internet connection. It suits businesses that prefer not to worry about server system maintenance and upgrades. Moreover, nothing stops an enterprise from using a combination of several cloud services to exploit the strengths of each in the multi-cloud solution. That’s why cloud platforms and serverless solutions may be attractive to:
- companies looking for cost-effective, scalable, and accessible data storage;
- businesses with remote employees who require seamless access to data;
- enterprises that prioritize data backup and recovery with minimal data loss.
In-house servers are the preference when you want complete control over your physical server and keep critical data on-site with no third-party access. This approach provides the security of knowing your data is physically present. On-premise hosting suits more to:
- organizations with a need for strict data security and control;
- businesses with legacy applications that must remain on on-site servers;
- companies with specific compliance requirements that necessitate in-house data management.
Hybrid cloud solutions offer the best benefits by combining in-house and cloud-based server options. This approach is suitable for enterprise cloud adoption strategy with diverse needs and circumstances. The most relevant cases to use hybrid models are:
- companies with legacy systems that require on-site servers while migrating other data to the cloud;
- businesses looking to extend processing power with the flexibility to send intensive tasks to the cloud while keeping sensitive data on-site;
- organizations with short-term peak loads that find cost savings in using the cloud for additional resources during these periods.
To determine which approach best aligns with your general business goals, consider the following:
- Specific needs
Evaluate your business’s unique requirements, such as remote work capabilities, office space limitations, power stability, and software compatibility. - Budget
Consider your budget, including upfront costs and ongoing expenses. In-house servers may involve significant initial investments, while the cloud typically offers lower upfront costs but ongoing subscription fees. - Internet connectivity
Both cloud infrastructure and hybrid solutions rely on a reliable internet connection. While a local network allows on-premise infrastructure to operate autonomously, modern businesses, in most cases, must provide uninterrupted access to the Web and traditional in-house servers.
Choosing between cloud infrastructure, in-house servers, or a hybrid model should align with your business purposes, data security needs, and financial considerations. It’s essential to assess your situation carefully and, when in doubt, seek expert advice to make an informed decision.
Practice shows that the hybrid model in modern conditions provides the greatest flexibility for creating company IT resources, ensuring cross-platform integration of various information systems. An example of this approach is the AI system we developed for real estate, which combines the computing power of the cloud and different local servers with data.

Cloud AI-driven real estate application
Make a Decision Cloud vs Hosted Server with Academy Smart’s Assistance
Leveraging our expertise in custom software development, Academy Smart offers a comprehensive approach to implementing cloud adoption strategy for enterprise customers. Our IT outstaffing services ensure you will get skilled programmers and DevOps for the development and maintenance of the hybrid cloud-based applications. Get in touch to share your project vision and specifications.
Frequently Asked Questions: Cloud vs In House Servers
Which is better, in-house servers or cloud computing?
The choice between in-house servers and cloud computing depends on your business aims and priorities. In-house servers offer greater control and security but come with higher initial costs, while cloud computing provides scalability and flexibility at the expense of some control.
What are hybrid clouds and multi-cloud?
Hybrid clouds combine private and public cloud infrastructure, offering a mix of on-premises control and cloud scalability. Multi-cloud refers to using multiple public cloud providers for different purposes, which can enhance redundancy and flexibility but may increase management complexity.
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!