What is the Difference Between Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Architecture
Contents
The choice between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud architectures has become critical for companies aiming to balance agility, scalability, and control. Its complexity arises from optimizing costs, enhancing performance, and ensuring data security in an environment where one-size-fits-all solutions fall short. This article clarifies the difference between hybrid and multi-cloud approaches to help enterprises craft an IT strategy that aligns with their unique needs.
Hybrid Cloud Architecture Specific
Hybrid cloud, in essence, merges the strengths of on-premise infrastructure, public cloud, and private clouds to form a cohesive and versatile computing environment. Unlike a singular public or private cloud, the pragmatic hybrid model allows enterprises to leverage both benefits, fostering flexibility, optimal resource utilization, and effective management control.
This architecture typically involves a combination of at least one private and one public cloud, orchestrated to meet specific business needs. For example, a company may run critical applications on a private cloud for security and compliance, while utilizing the scalability of a public cloud during peak demand.
The distinguishing feature of a hybrid cloud lies in its ability to seamlessly integrate different cloud environments, ensuring a unified approach to managing tasks across public and private clouds. This orchestration is crucial for optimizing workloads, taking advantage of public clouds’ increased power and resources, and adapting to fluctuating demand through techniques like cloud bursting.
Businesses opt for a hybrid cloud strategy for various reasons, including balancing costs, enhancing scalability, ensuring security and compliance, and improving overall business agility. It allows organizations to strategically choose where to host specific workloads, providing a blend of security and flexibility that may be challenging to achieve with a single cloud approach.
However, it’s essential to acknowledge the challenges associated with hybrid cloud adoption. Configuring, deploying, and managing hybrid environments can be more complex than a single-cloud model. Security concerns may arise, especially if data protection measures are not diligently implemented. Additionally, disruptions in the connection between private and public cloud services could impact operations, emphasizing the importance of robust management practices and careful consideration of costs.
Multi-Cloud Architecture Peculiarity
Multi-cloud architecture is a strategic approach that utilizes two or more public cloud services from different providers to meet the diverse IT needs of an enterprise. That contrasts with a single-cloud approach, enabling businesses to select the most suitable cloud services for different workloads. The primary advantage lies in its flexibility, allowing organizations to avoid vendor lock-in and capitalize on the strengths of various cloud providers.
One key aspect of multi-cloud is the dispersion of cloud-based assets, software, and applications across different cloud environments. This mix-and-match technique allows companies to maintain specific infrastructure for diverse workloads. Unlike hybrid cloud architectures, where processes and data may mix and interconnect, multi-cloud environments generally operate in silos, with each cloud managing a specific workload independently.
Commonly associated with major public cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, and others, multi-cloud setups allow enterprises to choose services based on cost, technical requirements, geographic availability, and other factors. It might involve using one cloud provider for development, another for disaster recovery, and yet another for processing business analytics data.
Multi-cloud strategies offer several benefits, including the ability to select the best services for each task, potentially lower costs compared to a private cloud setup, flexible and scalable environments, increased backup and redundancy options, and the freedom to choose public cloud and connectivity providers. However, enterprises adopting multi-cloud architectures must be mindful of potential challenges, such as the complexity of managing multiple providers, security concerns if handled poorly, and cost model variations among different cloud vendors. To manage multiple cloud assets effectively, you may need reliable and functional tools like Cloudyn, which our team participated in developing.

Cloud management application Cloudyn
Multi-cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud Comparison
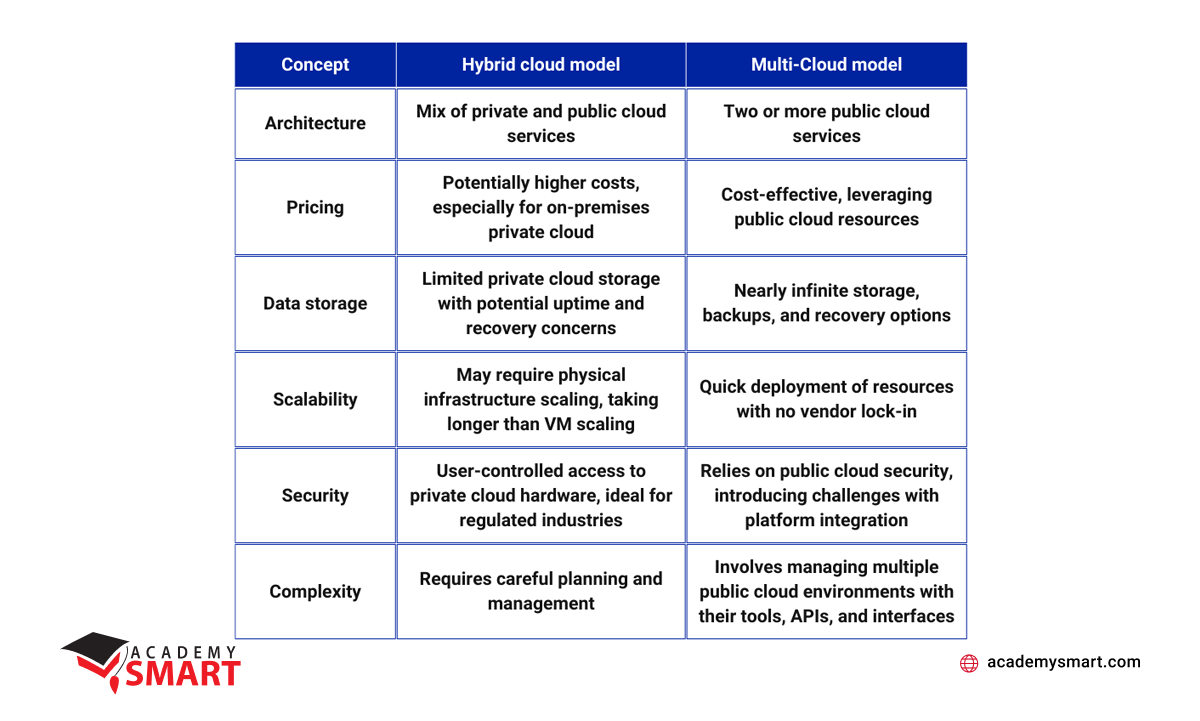
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud architectures are two distinct models in cloud computing, each offering unique advantages and considerations.
Architecture
Hybrid cloud combines private and public cloud services, allowing organizations to own and manage a private cloud resource while syncing with public cloud workloads. In contrast, multi-cloud exclusively uses two or more public cloud services from different providers, with no private cloud in the mix. Multi-cloud architectures operate independently, while hybrid clouds aim to integrate private and public resources seamlessly.
Pricing
Hybrid clouds may incur higher costs if the private cloud resource is hosted on-premises. The initial investment, management, and maintenance of private resources contribute to these expenses. Multi-cloud solutions, leveraging public cloud resources, are generally more cost-effective. The economies of scale public cloud vendors offer make multi-cloud deployment affordable and flexible.
Availability
Multi-cloud environments are designed for high availability, with public cloud resources ensuring business-critical uptime. In case of a failure, services can quickly switch to another cloud. In hybrid clouds, downtime may occur if the private resource requires maintenance, and the availability is contingent on managing the private component effectively.
Data storage
Hybrid clouds excel in managing sensitive data, providing a finite but secure space for critical information. Conversely, multi-cloud offers almost infinite storage space, extensive backup possibilities, and enhanced disaster recovery options. The choice between the two depends on the enterprise’s data storage needs and regulatory compliance requirements.
Security
Hybrid clouds offer control over physical access to private cloud hardware, appealing to highly regulated industries. Multi-cloud relies on the security features of each public cloud provider, potentially introducing security challenges associated with integrating different platforms. Both models prioritize security, but the approach differs, with hybrid focusing on user-controlled hardware access and multi-cloud relying on state-of-the-art public cloud security.
Flexibility
Multi-cloud solutions are flexible, allowing businesses to choose resources based on specific needs and avoiding vendor lock-in. Hybrid clouds also offer flexibility, combining private and public cloud advantages, but it may be more limited in terms of private cloud resource choices.
Complexity
Multi-cloud complexity lies in managing several public cloud environments, each with its tools and interfaces. Hybrid clouds require integration and management of both private and public components, ensuring data consistency and security across the hybrid infrastructure.
In conclusion, the choice between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud depends on cost considerations, data storage needs, regulatory compliance, security preferences, flexibility requirements, and IT department expertise. Each architecture has advantages and complexities, and companies should carefully assess their specific needs before adopting either model. Moreover, their combination has no obstacles if the project requirements request it.
Hybrid vs multi cloud
Build Your Enterprise Cloud Architecture with Academy Smart
We specialize in migrating enterprise applications to the cloud, developing cloud-native apps, and engineering hybrid and multi-cloud solutions utilizing Amazon and Azure services. Our team has solid microservices, containerization, and cloud infrastructure expertise, providing expert support to elevate your workforce or assemble a dedicated development team. Contact us to ensure your business’s cloud computing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions: Difference Between Multi Cloud and Hybrid Cloud
Why do many organizations use the hybrid and multi-cloud approach?
They opt for the hybrid and multi-cloud approach to leverage the tailored benefits of private and public clouds, balancing control, security, and scalability while avoiding vendor lock-in and ensuring flexibility in resource utilization.
What is the difference between multi cloud and hybrid cloud?
The main difference lies in their architecture: hybrid cloud combines private and public cloud services, whereas multi-cloud involves using two or more public cloud services without necessarily incorporating a private cloud.
Book a free consultation

Reach out to start talking today!